Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a strain of the Cannabis sativa plant species that is grown specifically for the industrial uses of its derived products. It is one of the fastest growing plants and was one of the first plants to be spun into usable fiber 10,000 years ago.
Hemp has lower concentrations of THC and higher concentrations of cannabidiol (CBD), which decreases or eliminates its intoxicating effects.
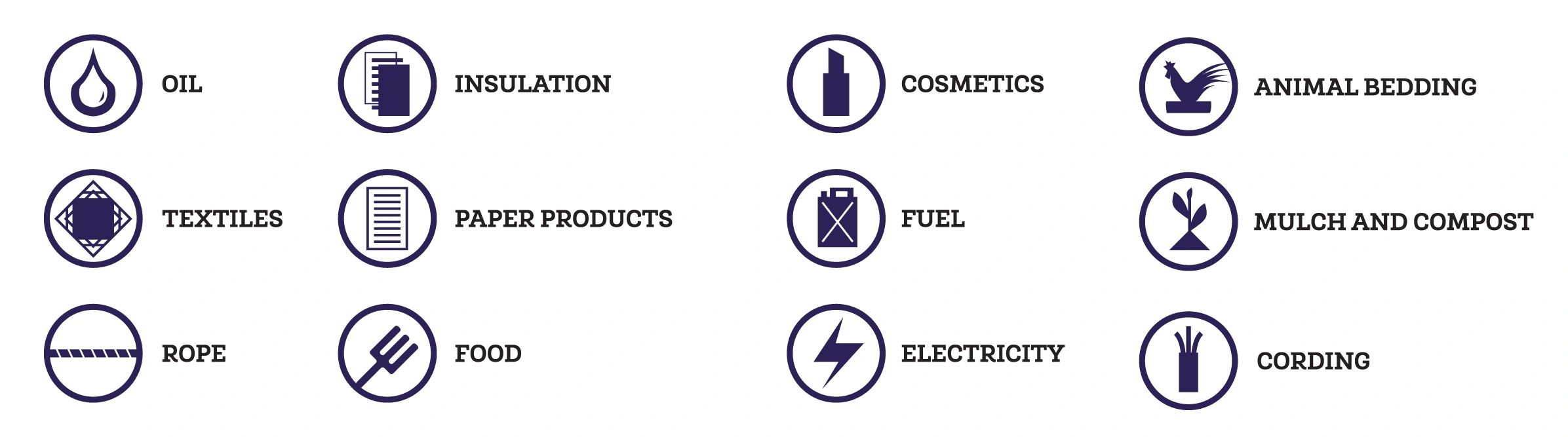
The Many Uses of Hemp

Commercial
Hemp Benefits
Commercial

Industrial
Hemp Benefits
Commercial

Hemp Benefits
Hemp Benefits
Hemp Benefits
Nutrition
A 100-gram portion of hulled hemp seeds supplies:
- 586 calories
- 5% water
- 5% carbohydrates
- 49% total fat
- 31% protein
Hemp seeds are notable in providing 64% of the Daily Value (DV) of protein per 100-gram serving. Hemp seeds are a rich source of dietary fiber (20% DV), B vitamins, and the dietary minerals manganese (362% DV), phosphorus (236% DV), magnesium (197% DV), zinc (104% DV), and iron (61% DV). About 73% of the energy in hempseed is in the form of fats and essential fatty acids, mainly polyunsaturated fatty acids, linoleic, oleic, and alpha-linolenic acids. The ratio of the 38.100 grams of polyunsaturated fats per 100 grams is 9.301 grams of omega‑3 to 28.698 grams of omega‑6. Typically, the portion suggested on packages for an adult is 30 grams, approximately three tablespoons.
Hempseed's amino acid profile is comparable to other sources of protein such as meat, milk, eggs and soy. Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores (PDCAAS), which attempt to measure the degree to which a food for humans is a "complete protein", were 0.49–0.53 for whole hemp seed, 0.46–0.51 for hempseed meal, and 0.63–0.66 for hulled hempseed.
